can low carbon steel be hardened by quenching Hardening tempering heat annealing quenching induction treating engineering carburizing sst treated efactory vacuum
Quenched and Tempered Alloy Steels [Usage and Properties]
Overview
 Quenched and tempered alloy steels are a group of high-strength steels that are widely used in various industries due to their exceptional mechanical properties. These steels undergo a specific heat treatment process known as quenching and tempering, which enhances their hardness, strength, and toughness. This treatment involves heating the steel to a specific temperature, followed by a rapid cooling process and subsequent reheating to a controlled temperature. The resulting material exhibits superior strength, wear resistance, and fatigue strength.
Quenched and tempered alloy steels are a group of high-strength steels that are widely used in various industries due to their exceptional mechanical properties. These steels undergo a specific heat treatment process known as quenching and tempering, which enhances their hardness, strength, and toughness. This treatment involves heating the steel to a specific temperature, followed by a rapid cooling process and subsequent reheating to a controlled temperature. The resulting material exhibits superior strength, wear resistance, and fatigue strength.
Applications
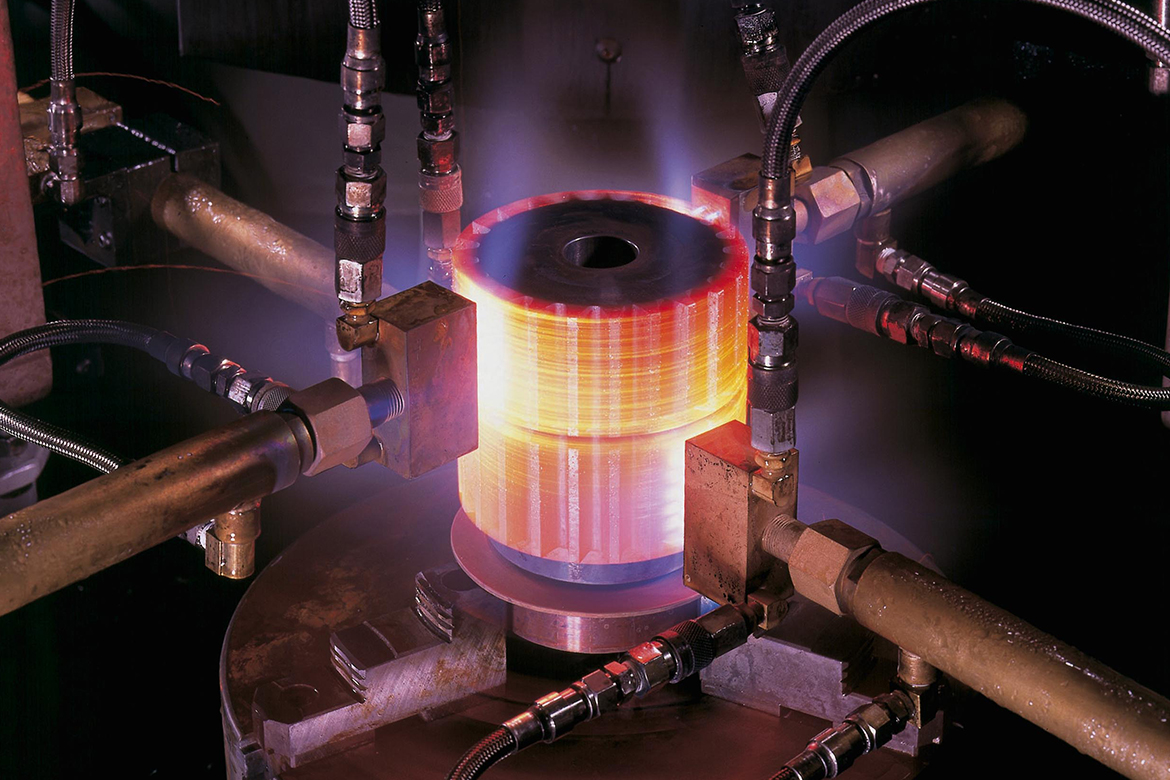 Due to their unique properties, quenched and tempered alloy steels find extensive applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and oil and gas. These steels are commonly used in the manufacturing of critical components, including gears, shafts, axles, springs, and structural parts. They are particularly suitable for applications requiring high strength, durability, and resistance to wear and impact. Moreover, their excellent heat resistance makes them ideal for use in elevated temperature environments.
Due to their unique properties, quenched and tempered alloy steels find extensive applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and oil and gas. These steels are commonly used in the manufacturing of critical components, including gears, shafts, axles, springs, and structural parts. They are particularly suitable for applications requiring high strength, durability, and resistance to wear and impact. Moreover, their excellent heat resistance makes them ideal for use in elevated temperature environments.
Properties
Quenched and tempered alloy steels exhibit several desirable properties that make them highly sought after in various industries:
- High Strength: These steels possess exceptional strength, allowing them to withstand heavy loads and resist deformation.
- Hardness: The heat treatment process significantly increases the hardness of the steel, providing excellent resistance to abrasion and wear.
- Toughness: Despite their high strength, these steels retain good toughness, which enables them to absorb energy and resist fracture under impact or shock loading.
- Fatigue Strength: The unique microstructure obtained after the quenching and tempering process enhances the fatigue strength of these steels, making them well-suited for applications subjected to cyclic loading.
- Machinability: Although quenched and tempered alloy steels are generally harder to machine compared to mild steels, they still offer reasonable machinability when proper cutting tools and techniques are employed.
Conclusion
Quenched and tempered alloy steels are invaluable materials in modern engineering due to their exceptional mechanical properties. The heat treatment process provides them with high strength, hardness, and toughness, making them ideal for a wide range of applications in various industries. From critical components in automotive and aerospace to structural parts in construction and oil and gas, these steels play a crucial role in ensuring the reliability and performance of numerous engineering systems. With their ability to withstand heavy loads, resist wear and impact, and exhibit excellent fatigue strength, quenched and tempered alloy steels continue to be the preferred choice for many professionals in the field.
If you are searching about flame hardening on low carbon steel you’ve visit to the right page. We have 5 Pictures about flame hardening on low carbon steel like Quenched and Tempered Alloy Steels [Usage and Properties], Heat Treatments - TURCONT - Cnc Machining Services and Casting Foundry and also How Quenching Hardens Steel in Metalworking. Here you go:
Flame Hardening On Low Carbon Steel
 www.slideshare.nethardening
www.slideshare.nethardening
Quenched And Tempered Alloy Steels [Usage And Properties]
![Quenched and Tempered Alloy Steels [Usage and Properties]](https://www.engineeringworldchannel.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/20200720111837_download-1-768x529.jpg) www.engineeringworldchannel.comsteels quenched structural commonly
www.engineeringworldchannel.comsteels quenched structural commonly
How Quenching Hardens Steel In Metalworking
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/germany--munich--foundry-worker-pouring-hot-metal-into-cast-515029441-5c5ef3e1c9e77c0001d31cd2.jpg) www.thoughtco.comquenching ductility metalworking foundry logam westend61 ductile pouring
www.thoughtco.comquenching ductility metalworking foundry logam westend61 ductile pouring
Heat Treatments - TURCONT - Cnc Machining Services And Casting Foundry
 turcont.comhardening tempering heat annealing quenching induction treating engineering carburizing sst treated efactory vacuum
turcont.comhardening tempering heat annealing quenching induction treating engineering carburizing sst treated efactory vacuum
What Makes Quenched Steel So Hard? - Knife Steel Nerds
 knifesteelnerds.comquenched microstructure schematic quenching principles metallurgy
knifesteelnerds.comquenched microstructure schematic quenching principles metallurgy
Hardening tempering heat annealing quenching induction treating engineering carburizing sst treated efactory vacuum. Quenched microstructure schematic quenching principles metallurgy. What makes quenched steel so hard?